Subscribe to the Zog Blog to get news Delivered straight to Your box!
Newsletter Signup
Recent Posts
Archives
Archives
- May 2025 (1)
- March 2025 (1)
- November 2024 (1)
- October 2024 (1)
- August 2024 (1)
- July 2024 (1)
- June 2024 (1)
- May 2024 (1)
- December 2023 (2)
- November 2023 (1)
- August 2023 (1)
- June 2023 (1)
- May 2023 (1)
- April 2023 (1)
- December 2022 (4)
- November 2022 (3)
- October 2022 (2)
- September 2022 (2)
- August 2022 (3)
- July 2022 (2)
- May 2022 (3)
- April 2022 (2)
- March 2020 (1)
- November 2019 (1)
- October 2019 (2)
- September 2019 (3)
- August 2019 (2)
- July 2019 (5)
- June 2019 (3)
- May 2019 (2)
- April 2019 (1)
- March 2019 (2)
- August 2018 (2)
- July 2018 (1)
- June 2018 (1)
- May 2018 (4)
- April 2018 (5)
- March 2018 (2)
- February 2018 (3)
- January 2018 (3)
- December 2017 (3)
- November 2017 (2)
- October 2017 (3)
- September 2017 (4)
- August 2017 (2)
- July 2017 (4)
- June 2017 (4)
- May 2017 (5)
- April 2017 (4)
- March 2017 (3)
- February 2017 (4)
- January 2017 (5)
- December 2016 (4)
- November 2016 (5)
- October 2016 (4)
- September 2016 (3)
- August 2016 (4)
- July 2016 (1)

Zog’s Ultimate Guide to Cybersecurity: A Resource for Beginners
Cybersecurity is a rapidly evolving area of focus, investment, and concern for businesses of all sizes.
For small and medium sized businesses in particular, cybersecurity has become even more critical. While larger companies typically have the resources to invest in robust and proactive security measures, smaller businesses often struggle to keep up. This was the primary motivation behind creating Zog’s Ultimate Guide to Cybersecurity.
This guide serves as a comprehensive, up-to-date resource for anyone hoping to learn about threats and how to best prevent them.
Get ready to arm yourself with the latest in cybersecurity defenses.
Let’s dive in.
Jump to a Specific Section
>>What is Cybersecurity?
>>Why is Cybersecurity Important?
>>What are the Most Common Types of Cyber Attacks and Threats?
>>Cybersecurity Basics for Beginners
>>What is a Managed Security Service Provider (MSSP)?
>>Cybersecurity Definitions, Resources, and Statistics
>>Cybersecurity Podcasts to Bookmark
>>Cybersecurity Blogs to Bookmark
>>Must Know Cybersecurity Stats
>>Starting a Career in Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity: What is It Exactly?
Cybersecurity is all about protecting data from malicious attacks, unauthorized access, and manipulation. It encompasses a wide range of topics including network, mobile, application, and data security.
With so many attacks stemming from human error, successful cybersecurity programs account for this. Education built around recognizing and responding to threats and good cyber hygiene help stay ahead of human error.
Why is Cybersecurity Important?
Cybersecurity is important because it helps protect your business (company, financial, customer, and employee data) from cyber threats. Unseen or unprotected, these threats can have devastating consequences.
What are the Most Common Types of Cyber Attacks and Threats?
Malware
Short for malicious software, malware refers to programs or code designed to harm, infiltrate, or disrupt computer systems.
Malware can take many forms including viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, spyware, and adware. It can be spread via email attachments, software downloads, infected websites, or online ads. Malware can cause problems from minor annoyances like unwanted pop-ups to serious issues like data breaches and financial loss.
Examples of malware include WannaCry ransomware, NotPetya malware, and Zeus Trojan.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attack
A man-in-the-middle attack (MitM) is a form of cyber attack where an attacker intercepts communication between two parties to eavesdrop, steal information, or manipulate the conversation. The attacker positions themselves in the middle of the communication flow between two devices or users, making it appear as though they are communicating with each other. It is often done through the use of malware, phishing, or other social engineering tactics.
For example, a hacker may create a fake Wi-Fi hotspot in a public coffee shop and trick unsuspecting users into connecting to it. Once connected, the attacker can intercept all communication between the user and the internet, including sensitive information like login credentials or banking information. Another example is using a fake website that looks like a legitimate one to steal login credentials, such as banking or email passwords. To protect against MitM attacks, it is recommended to use secure communication protocols, such as HTTPS, and to be cautious when connecting to unknown networks or websites.
Phishing
Phishing is a type of cyberattack where individuals are tricked into sharing sensitive information such as passwords, credit card details, and other personal information. These attacks typically appear to originate from legitimate, reputable sources and is most commonly conducted via email and social media messages.
Phishing attacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated and more and more difficult to detect. Attackers use psychological tactics to lure victims into clicking links or downloading attachments, which once clicked or downloaded and personal information is obtained, can then be used for malicious purposes like identity theft or financial fraud.
To protect from phishing attacks, be alert of suspicious emails or messages and always verify the sender’s authenticity before sharing personal, potentially sensitive information.
Drive-By Downloads
Drive-by downloads refer to malicious software downloads that take place without a person’s knowledge or consent and can be triggered when visiting a compromised website or clicking a malicious link. The download can access sensitive information, login credentials, and even compromise entire systems.
For example, a person may unknowingly download malware onto their device by clicking on a pop-up while browsing the internet or visit a seemingly harmless website that has been compromised by hackers, resulting in a drive-by download of malware onto their device.
To protect against drive-by downloads, keep software and security systems up to date and exercise caution when clicking on links or downloading software from unknown sources.
Password Attacks
Password attacks are malicious attempts hackers make to gain access to an individual’s or organization’s data. These attacks are often carried out by automated tools and techniques such as brute force, dictionary, keylogger, phishing, and social engineering attacks with the goal of guessing or cracking passwords.
Password attacks typically result in data and financial loss, identity theft, and reputational damage.
To prevent password attacks, adopting strong password policies is a must and should include regular password changes, two-factor authentication, and regular, ongoing employee training.
DDoS
A DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attack is a cyberattack that aims to disrupt a targeted website or network by overwhelming it with traffic. DDoS attacks are achieved by using a network of compromised devices (referred to as a botnet) to simultaneously flood the target with massive amounts of traffic, making it inaccessible to legit visitors.
Examples of recent DDoS attacks include attacks on Github, Dyn, and KrebsOnSecurity.
Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malicious software that encrypts a victim’s files and demands ransom (payment) in exchange for a decryption key. Cybercriminals use various methods to deliver ransomware, such as phishing emails, drive-by downloads, and by exploiting vulnerabilities in software. Once the ransomware infects the victim’s system, it can quickly spread throughout the network, causing significant damage to personal and business data.
Examples of well-known ransomware include WannaCry and Petya. Ransomware attacks can have severe consequences such as loss of data, disruption of operations, and financial damages. Protecting against ransomware involves implementing strong security measures, regular backups, and employee education on cybersecurity best practices.

Cross Site Scripting
Cross Site Scripting (XSS) refers to the injection of malicious code into seemingly trustworthy websites. Code is typically injected through input fields or URLs and can lead to sensitive data being compromised.
For example, an attacker could inject a script that steals login information when the victim enters it into a compromised website login form. An attacker could also inject a script that redirects unsuspecting visitors to a phishing site that looks nearly identical to the original website. XSS attacks can be persistent or non-persistent depending on whether malicious code is stored on the server or sent with each request.
To protect against cross site scripting, web developers should implement input validation and sanitization while also using security headers like a content security policy (CSP).
SQL Injection
Structured Query Language (SQL) is a programming language used to manage and manipulate data in a database. SQL injections are a type of cyber attack in which an attacker injects malicious SQL code into a vulnerable website or application with the intention of gaining access to or modifying sensitive data stored in a database.
An attacker can use an SQL injection to bypass login credentials, steal personal or financial data, modify or delete data, and even take control of the entire website or application.
For example, if an attacker injects a malicious SQL query into a login form, they can bypass the authentication process and gain access to the website’s backend database, which likely stores user login credentials and other sensitive information.
To prevent SQL injections, developers should validate user inputs, use prepared statements, and restrict database permissions. Web application firewalls can also be used to detect and block SQL injection attacks.
How to Identify Cyber Threats
One of the most common ways to identify cyber threats comes by way of your network traffic logs. Monitoring these logs can help identify unusual activity and/or patterns that indicate an attack took or is currently taking place. It is also important to keep systems and software up-to-date, further helping prevent vulnerabilities cybercriminals live to exploit.
Staying informed about the latest cybersecurity trends and threats is also crucial. Reading cybersecurity blogs, attending webinars, and following cybersecurity experts on social media are all great ways to stay informed.
Routine security assessments are another means of staying ahead of cyber threats and can be conducted by in-house cybersecurity experts or outsourced to third-party security and digital forensics firms.
Cybersecurity experts also recommend regular use of tools like firewalls, antivirus, and intrusion detection systems which help detect and prevent threats by monitoring network traffic and flagging suspicious activity. Implementing and enforcing security policies while regularly training employees is also a must when thinking about how to go about identifying cyber threats.
What Industries are Most Vulnerable to Cyberattacks in 2023?
Cyberattacks in Healthcare
An industry most vulnerable to cyberattacks in 2023 is the healthcare industry. With increasing use of electronic health records and the digitization of medical devices, healthcare providers are at an incredibly high risk of cyberattacks. Cybercriminals aim to steal sensitive patient data, manipulate medical records, and even hack into medical devices, putting patient lives at risk.
Cyberattacks in Finance
Another industry highly vulnerable to cyberattacks is the financial industry. Cybercriminals obsess over finding ways to maliciously access financial systems and steal valuable financial data. With the ever increasing use of mobile banking, ecommerce, and online payment systems, financial institutions are a prime target for cybercriminals and attacks.
Cyberattacks in Transportation
Growing use of autonomous vehicles, connected transportation systems, and airlines all serve as targets for cybercriminals and put the transportation industry on the list. Once systems are accessed, cybercriminals can cause accidents, disrupt transportation systems and supply chains, and even steal sensitive transportation data.
Cyberattacks in Energy
The energy sector is consistently at risk of cyberattacks. Hackers target power grids and other critical infrastructure, causing blackouts and other potentially devastating disruptions. This leads to serious public safety and national security concerns.
Cyberattacks in Retail
Retail is another industry prone to cyberattacks as they handle massive volumes of customer data such as credit card information, physical addresses, and contact details. Hackers will aim to gain access to this information which they can then turn and sell on the dark web for a profit.
It’s incredibly important for businesses in these industries to take proactive steps to protect themselves and those they service.
Cybersecurity Basics for Beginners
Protecting your business from cyber threats starts with understanding the basics.
Experts Chime in on Cybersecurity Best Practices
The team at Zog recently interviewed a group of cybersecurity experts and asked them to share some of the biggest mistakes they see businesses making when it comes to cybersecurity.
Menny Barzilay, Partner & Co-Founder at Cytactic shined light on the importance of keeping cybersecurity top of mind, regardless of your business type. Every business is a potential target for hackers.

Ann Marie Fred (@DukeAMO), Software Engineer & Security Lead shared actionable insight any business in any industry can apply in less than one week. When it comes to cybersecurity, hope is not a defense.

Scott Schober (@ScottBVS), President & CEO of Berkeley Varitronics Systems doubles down on the importance of passwords – password policies, strong passwords, not reusing passwords, and the value of two-factor authentication.

Sean Wright (@SeanWrightSec), Experienced Application Security Engineer shared his take on the importance of prioritization and organization when it comes to managing cybersecurity. Focusing on what matters most is key as Sean puts it.

Marc-Roger Gagné MAPP (@OttLegalRebels), Privacy Advocate, Cybersecurity, and Director at Interfima passed along valuable and actionable information relating to the importance of businesses taking cybersecurity as seriously as they take their growth.

Protecting Your Organization from Cyber Threats
Here are a few cybersecurity tips to help protect against cyber threats:
Monitoring Your Network
Just as important as it is when thinking about identifying threats, monitoring your network is equally essential when it comes to protecting your organization from cyberthreats. Monitoring regularly and routinely for suspicious activity such as unauthorized access or malicious code can mean the difference between keeping your data and business secure and falling victim to an attack.
Staying Secure While Working Remotely
Cybercriminals work hard to exploit vulnerabilities in remote work environments and it is up to employees to remain vigilant and do their part in helping prevent data breaches and other security threats.
One of the simplest but often overlooked steps remote employees can practice is only accessing secure networks. Avoid public Wi-Fi networks and ensure home networks are secured via strong passwords and two-factor authentication when possible. Virtual private networks (VPN) will also encrypt internet connections and help protect sensitive data.
Another step remote workers can take and that their employers should enforce is the use of secure devices and software. Employers should ensure their employees’ laptops, smartphones, tablets, etc. are updated with security patches and antivirus software while practicing caution when downloading apps or software.
Cybersecurity Training for Employees
Employee training is an important part of protecting your business from cyber threats. All employees should be trained on cybersecurity best practices, such as recognizing and responding to phishing attacks, creating strong passwords, and understanding the importance of good cyber hygiene. Additionally, all employees should receive regular training to ensure they are up-to-date on the latest cybersecurity threats, preventative measures, and best practices.
Cybersecurity Tools for Beginners
There are numerous cybersecurity tools available that help businesses protect their sensitive data, networks, and systems from cyber threats. Tools range from antivirus software and firewalls to encryption and multi-factor authentication solutions. We’ll break each of the tools down below.
Antivirus & Cybersecurity
One of the most important tools for businesses thinking proactively about cybersecurity is antivirus software. Antivirus software detects and removes malicious software such as viruses and malware from a computer or network. It also helps prevent future infections by blocking suspicious files and URLs. There are many antivirus software options available, ranging from free to paid versions, depending on the level of protection desired or required.
Firewalls & Cybersecurity
Firewalls are another important cybersecurity tool for businesses. A firewall acts as a barrier that sits between a network and the internet and monitors and blocks incoming and outgoing traffic based on predefined rules. A firewall helps prevent unauthorized access to networks while protecting against malware and other cyber threats and can be hardware or software-based.
Encryption & Cybersecurity
Encryption is another cybersecurity essential for any business aiming to prevent unauthorized access to data and networks and is the process of converting sensitive data into an unreadable format that can only be decoded with a special key. This ultimately helps protect data from unauthorized access and ensure its confidentiality. There are many encryption solutions available, including full-disk encryption and file-level encryption.
Multi-Factor Authentication & Cybersecurity
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is another mechanism businesses deploy when protecting data and preventing unauthorized access – even when a password is compromised – is the goal. MFA is a process which requires a user to provide two or more authentication factors (password + biometrics / fingerprint or password + code from authentication app) in order to access data, a system, or an application.
Virtual Private Networks & Cybersecurity
Virtual private networks (VPN) create secure and encrypted connections between corporate devices and the internet, helping defend against hackers aiming to access or intercept data as it travels the internet. VPNs are especially beneficial when employees access the internet remotely.
Security Information & Event Management (SIEM) & Cybersecurity
Security information and event management (SIEM) systems monitor and analyze security events in realtime. SIEM systems detect and respond to suspicious activities, unauthorized access attempts, and malware infections for example.
Password Policies
Where there’s a password, there’s a cybercriminal trying to crack it. Password policies are a set of guidelines designed to prevent unauthorized access and ultimately dictate how passwords are created, used, and managed within an organization. Password policies typically address password strength, uniqueness, and shelf-life.
When thinking about passwords, one of the best policies is to require strong passwords which usually include upper and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Passphrases are another common suggestion in password policies as they allow for more complex passwords that aren’t as forgettable as traditional letter, number, character combinations.
Length is strength when it comes to passwords.
What is a Managed Security Service Provider (MSSP)?
A managed security service provider (MSSP) is a third-party highly specialized and experienced in providing cybersecurity services to companies. MSSPs provide a range of services such as monitoring, backup and disaster recovery, consulting, risk assessments, security architecture design, vulnerability scanning, and managed firewall.
Businesses save time and money while gaining control over their IT infrastructure when outsourcing their cybersecurity to an MSSP.
What are the Benefits of Partnering with a Managed Security Service Provider?
Aside from cost savings, there are many benefits to take into consideration when choosing an MSSP. Here are some of the most common ones:
- 24/7 monitoring: MSSPs will offer extreme peace of mind as they typically provide 24/7 monitoring and will alert businesses of suspicious activity.
- Expertise: MSSPs employ teams of security and technology experts who have vast industry knowledge and experience.
- Efficiency: Businesses can grow more efficient as they automate otherwise manual processes and streamline security operations.
- Scalability: MSSPs can easily grow as you grow, scaling their services to meet the evolving needs of the business and its employees.
- Compliance and regulatory: When compliance is non-negotiable, MSSPs will ensure compliance and regulatory requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, and DFARS are met.
What types of services do the best cybersecurity companies offer?
The best cybersecurity companies or MSSPs will most certainly offer levels of endpoint protection and threat monitoring, detection, and management. What this will entail is continuous network monitoring for suspicious activity and immediate response if and when a threat is identified. MSSPs accomplish this via the utilization of advanced threat monitoring and intelligence tools, expert staff, and routine analysis.
Another service most MSSPs will offer is vulnerability management, which typically involves the identification and prioritization of network and systems vulnerabilities via automated vulnerability scanning tools and manual audits. Once assessed, MSSPs will devise strategies to mitigate risk and address weak points throughout a business’s digital infrastructure.
Incident response is another commonly sought after and offered cybersecurity service. As the inevitability of cyberattacks grows and businesses are more and more at risk, an MSSPs incident response team will help contain threats and minimize damage. Incident response teams will also conduct a post-event investigation with the goal of identifying the root cause of the incident, aiming to prevent it from happening again.
Cybersecurity Definitions, Resources, and Statistics
Definitions
What is Cybersecurity Awareness Month (CSAM)?
Every October, Cybersecurity Awareness Month aims to raise cybersecurity awareness across the country. During CSAM, activities and events like webinars, workshops, and online training courses provide knowledge and skills needed to minimize cyber risk.
Companies can use Cybersecurity Awareness Month to educate and reinforce cybersecurity policies with employees while individuals use it as an opportunity to practice good cyber hygiene, learn about the latest cyber threats, and ensure they know how to protect their personal information.
Ultimately, Cybersecurity Awareness Month helps create a safer and more secure digital world for everyone.
What is the CIA Triad?
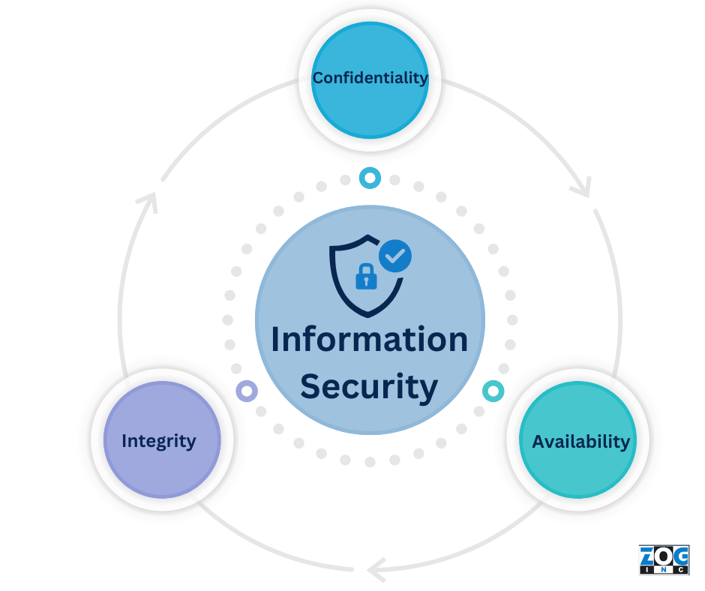
The CIA Triad is a widely used methodology in the information technology and security industries. It stands for confidentiality, integrity, and availability, which together form the foundation of information security and are used to ensure information is protected from unauthorized access, alteration, or destruction.
Confidentiality is the protection of sensitive data like credit card numbers, social security numbers, or medical records. Banks and hospitals might deploy encryption strategies to protect this data from unauthorized access.
Integrity represents the accuracy and consistency of data over its lifecycle. Digital signatures are often used to ensure important documents haven’t been tampered or altered with.
Lastly, availability refers to the ability to access data when needed. Backups of important or sensitive data take place to ensure data can be restored in the event of a disaster or cyberattack.
What is Authentication?
In cybersecurity, authentication is the process of verifying identities of individuals, devices, or systems attempting to access data or systems.
Authentication is a critical component of cybersecurity as it helps prevent unauthorized access and it can be done in various ways such as passwords, biometrics, security tokens, or multi-factor authentication.
What is a Backup?
Backups are the process of copying data to another location – either physical or virtual. Backups are typically stored in secure locations, either on-site, off-site, or in the cloud and can be used to restore data in case of a disaster or cyberattack. Businesses often perform regular backups of their servers and databases to prevent data loss while maintaining overall business continuity.
What is a Data Breach?
Data breaches are incidents where sensitive, oftentimes confidential information is exposed to unauthorized individuals. Hacking, malware, phishing, or even physical device theft may lead to a data breach where personal, financial, or corporate data is exposed.
In 2017, one of the largest credit reporting agencies in the United States suffered a data breach that exposed personal information of over 143 million customers.
What is Encryption?
Encryption is the process of converting plain text into a code or cipher so that it cannot be read by anyone who does not have the key to decode it.
Encryption is the process of converting plain text to code, accessible only to those with the key to decode it. In the realm of cybersecurity, encryption is a means of protecting sensitive data and is widely applied to digital transactions, email communications, and online banking.
What is IEC 62443?
IEC 62443 series of standards cover cybersecurity aspects like risk assessment, policies and procedures, network architecture, access control, and incident response. Organizations who comply with these standards ensure the security and reliability of their industrial automation and control systems (IACS) which are used in critical infrastructure sectors like energy, water, and transportation. Supervisory control and data acquisition systems (SCADA), distributed control systems (DCS), and programmable logic controllers (PLC) are examples of IACS systems.
What is SIEM in Cybersecurity?
Security information and event management (SIEM) refers to software that combines two security approaches – security information management (SIM) and security event management (SEM). SIEM solutions provide real-time monitoring, analysis, and alerting of security events happening within an organization’s tech infrastructure.
SIEM tools collect and analyze data from multiple sources and through analysis, can identify potential security threats and alert personnel to take action. Popular SIEM tools include Splunk, IBM Security QRadar, and AlienVault.
What is SOAR in Cybersecurity?
SOAR stands for security orchestration, automation, and response and is a comprehensive approach to cybersecurity involving automated data collected, analysis, and real-time security incident response. SOAR platforms streamline security operations and help teams detect and resolve threats more efficiently. For example, a SOAR platform will automatically analyze security tool alerts, determine severity, and initiate a response (isolating infected devices, blocking traffic, or initiating a forensic investigation).
SOAR technology has become increasingly popular in recent years due to the growing complexity and frequency of cyber threats.
What is NIST CSF?
NIST CSF stands for The National Institute of Standards and Technology Cybersecurity Framework and is a framework providing guidelines, best practices, and standards to manage and reduce cybersecurity risks.
The NIST CSF consists of five core functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. A hospital for example might use this framework to identify and protect patient data, detect security incidents, respond to those incidents, and recover from any damages caused by the incident.
What is EDR in Cybersecurity?
Endpoint detection and response (EDR) is a cybersecurity solution that detects and responds to advanced threats on endpoints. EDR solutions use behavioral analysis and machine learning to provide real-time visibility into endpoint activities, equipping security teams with information to contain threats faster.
Popular EDR solutions include CrowdStrike Falcon, Carbon Black, and Symantec Endpoint Detection and Response.
What is Whaling?
Whaling is a type of phishing attack aimed at senior executives and other high-profile individuals. Attackers study victims, their networks, and online behavior in preparation for crafting highly targeted, sophisticated, and personalized messages. Similar to phishing, whaling attacks aim to access sensitive data such as login credentials, financial documents, and sensitive employee information.
What is Smishing?
Smishing (SMS + phishing) is identical to phishing attacks, but instead of email as the message delivery mechanism, text or SMS is used. Just like phishing, the goal of a smishing attack is to convince victims to share sensitive data and/or click links resulting in malware downloads.
What is Vishing?
Vishing or voice phishing is another social engineering attack like phishing that instead uses phone calls and voice messages as the message delivery mechanism. A recorded message or automated voice system impersonating a legitimate person or organization tricks victims into taking action that often results in the compromise of sensitive data.
Best Cybersecurity Podcasts to Listen to in 2023
CyberWire Daily Podcast
Hosted by Dave Bittner and regularly featuring leading experts and security analysts, the CyberWire Daily Podcast is a must listen for anyone trying to stay on top of emerging threats, vulnerabilities, and industry trends. Tune in to new episodes every weekday.
Security Now!
Steve Gibson and Leo Laporte host the long-running Security Now! podcast which covers a variety of cybersecurity topics like encryption, privacy, and malware. The focus on technical details and analysis is what sets Security Now! apart from other cybersecurity podcasts. Tune in to this podcast if your aim is to deepen your understanding of cybersecurity.
Cyberlaw Podcast
Stewart Baker hosts the Cyberlaw Podcast which is a must bookmark for anyone interested in looking at cybersecurity through a legal lens. The Cyberlaw Podcast commonly features interviews with experts in law, policy, and technology, and when you couple that with Stewart’s Department of Homeland Security and NSA general counsel experience, this podcast is an excellent resource for cybersecurity and law professionals alike.
Darknet Diaries
Darknet Diaries is another must listen and offers a fascinating look into the world of cybercrime. Hosted by Jack Rhysider, the podcast tells stories of real-life cyberattacks as well as the people responsible for carrying out the attacks. Jack interviews hackers, researchers, and law enforcement officials, helping paint a vivid picture of the human side of cybersecurity.
Smashing Security
Smashing Security offers a laid back take on cybersecurity that is equally educational and entertaining. Graham Cluley and Carole Theriault team up to bring humor-injected weekly episodes that dive into cybersecurity news and trends.
Risky Business
Last on our list is Risky Business, a podcast hosted by Patrick Gray and Adam Boileau. In-depth analysis and expert commentary make this podcast an excellent resource for anyone aiming to understand how cyber attacks impact organizations.
Best Cybersecurity Blogs to Follow in 2023
Krebs on Security
Renowned cybersecurity journalist Brian Krebs hosts the Krebs on Security blog which covers a wide range of cybersecurity topics like cyber crime, data breaches, and online privacy. The blog stands out due to its deep level of analysis and is a must bookmark for anyone interested in cybersecurity.
Dark Reading
Dark Reading is another excellent blog that covers cybersecurity topics like threat intelligence, cloud security, and endpoint security. Cybersecurity and other industry experts contribute up-to-date trends and best practices, making Dark Reading an excellent and must read resource.
SC Media
A mix of news, analysis, and opinion pieces make SC Media a great resource for breaking news and in-depth analysis and ranks them third on our list of the best cybersecurity blogs.
Schneier on Security
Next on our list of the best cybersecurity blogs is Bruce Schneier’s Schneier on Security. Bruce is a cybersecurity expert and covers topics like cryptography, hacking, malware, cybercrime, and surveillance on his blog. You can expect deeply insightful analysis and resourceful content when visiting Schneier on Security.
SANS Institute
SANS Institute’s Cybersecurity Blog is packed with focus on cybersecurity with topics including threat intelligence, incident response, digital forensics, penetration testing, incident response, and network security. Instructors and industry experts provide regular updates on threats and vulnerabilities, making it easy for regular visitors to stay informed.
SecurityWeek
SecurityWeek offers cybersecurity news, insights, and analysis, covering topics like threat intelligence, compliance, and security architecture. Cybersecurity experts contribute to this must bookmark for those interested in staying on top of industry news and happenings.
The Hacker News
Last but not least on our list of the best cybersecurity blogs to follow in 2023 is The Hacker News. The Hacker News is a great resource for both breaking cybersecurity news as well as in-depth analysis, covering topics like vulnerabilities, attacks, data breaches, and more.
Must Know Cybersecurity Statistics in 2023
The Cost of Cybercrime is Growing
The projected cost of cybercrime is showing no signs of slowing down. According to a Cybersecurity Ventures report, cybercrime will cost the world $10.5 trillion annually by 2025. This is up from $3 trillion in 2015.

Phishing Attacks Remain a Concern
According to Deloitte, 91% of all cyberattacks start with a phishing email. Unexpecting victims are having a difficult time detecting these phishing emails as they come off more and more in the form of legitimate-looking emails.

Humans at the Center of Risk
A Gartner survey conducted in May and June of 2022 puts humans at the center of risk as it found 69% of 1,310 employees surveyed had bypassed their organization’s cybersecurity guidance in the past 12 months. In addition, 74% of the employees surveyed would be willing to bypass cybersecurity guidance to achieve business objectives.

Cloud-Based Attacks on the Rise
With the rise in adoption of cloud computing comes an increase in cloud-based attacks. According to Flexera’s 2021 State of the Cloud Report, 94% of enterprises are using cloud services, making it more important than ever to secure cloud environments.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Shaping the Cybersecurity Landscape
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) will continue to shape the cybersecurity landscape in 2023 and beyond. According to a MarketsandMarkets report, AI in the cybersecurity market is expected to grow globally to more than $38 billion by 2026. Organizations leverage AI and ML to detect and respond to threats faster than ever before.
The Cost of Ransomware is Growing Rapidly
The cost of ransomware is growing at a tremendous rate and for organizations of all sizes, simply cannot be ignored. A report by Cybersecurity Ventures shines light on just how much ransomware could cost businesses, expecting it to reach $265 billion by 2031.

How do you start a career in cyber security?
With the growing number of cyber threats and potentially devastating outcomes, companies and organizations are looking for skilled professionals who can safeguard their data. Gartner predicts that by 2025, lack of talent or human failure will be responsible for over half of significant cyber incidents. This in itself makes cybersecurity skills extremely in demand in the talent marketplace.
Like any career, starting a career in cybersecurity starts with a strong foundation in computer science, information technology, and network security. There are many colleges and universities that offer degree programs and certifications in cybersecurity – both in-person and online.
Once you’ve gained or are on your way to gaining that foundation in cybersecurity, hands-on, practical experience should follow. This is often accomplished through internships, apprenticeships, or entry-level roles in the field which not only offer valuable hands-on experience, but also the opportunity to work alongside and network with experienced professionals.
Another important step in starting a career in cybersecurity is to stay up-to-date with the latest trends and technologies in the field. Cybersecurity is a constantly evolving field, with new threats and vulnerabilities emerging all the time. To stay ahead of the game, stay informed about the latest developments in the field. This can be done by attending conferences, networking with other professionals in the field, or by reading industry publications.
Ongoing education and networking are musts, both early in your career and as you’re focusing on growing and evolving it. Cybersecurity is a constantly evolving field with new threats and vulnerabilities popping up every single day. Industry conferences make it possible to stay ahead of trends and growing threats while also providing the opportunity to network with other like-minded individuals in the industry. Professional organizations, online forums, and social networks are other alternatives to conferences.
What are the most common cybersecurity jobs?
The most common cybersecurity jobs or careers include security analyst, security engineer, security consultant, and security architect.
Security Analyst
Security analysts handle the day-to-day monitoring of networks, specifically for threats or red flags. In addition to monitoring company networks, security analysts identify breaches and contribute to ongoing cyberattack prevention strategies.
Security Engineer
Security engineers design and implement security systems and protocols and work cross-functionally with technical staff to ensure security measures are developed, deployed, and functioning properly.
Security Consultant
Security consultants are typically third-party professionals hired to assess a company’s security needs. In addition to recommending solutions, security consultants will often contribute to the deployment of solutions as well as provide training to employees on cybersecurity best practices.
Security Architect
Security architects design and implement cybersecurity solutions for entire organizations and work cross-functionally with other technology professionals to ensure their strategies are integrated throughout all aspects of a company’s technology infrastructure.
Penetration Tester
Penetration testers or ethical hackers are hired to seek and exploit vulnerabilities in an organization’s network by attempting to hack them, helping companies identify and fix weak points and vulnerabilities before malicious hackers have a chance to exploit them.
Policy and Governance
Not all cybersecurity professionals live in systems and code. Cybersecurity policy and governance professionals are hired to develop and implement the policies that ensure company data stays secure and ensure compliance with industry relevant regulations and standards.
Forensic Analyst
Forensic analysts gather evidence and investigate cybercrimes. They’ll often focus their efforts on analyzing data in hopes of identifying the source(s) of a cyberattack, helping law enforcement agencies and officials bring cybercriminals to justice.
Incident Response Specialist
Incident response specialists are often the first line of defense when a security breach takes place. They’ll respond to breaches and aim to mitigate impact. Working cross-functionally with other technical staff, incident response specialists work quickly to find the root cause of an attack while developing strategies to minimize damage and prevent future attacks.
Do Cyber Security Jobs Pay a Good Salary?
The average cybersecurity salary is well above the national average.
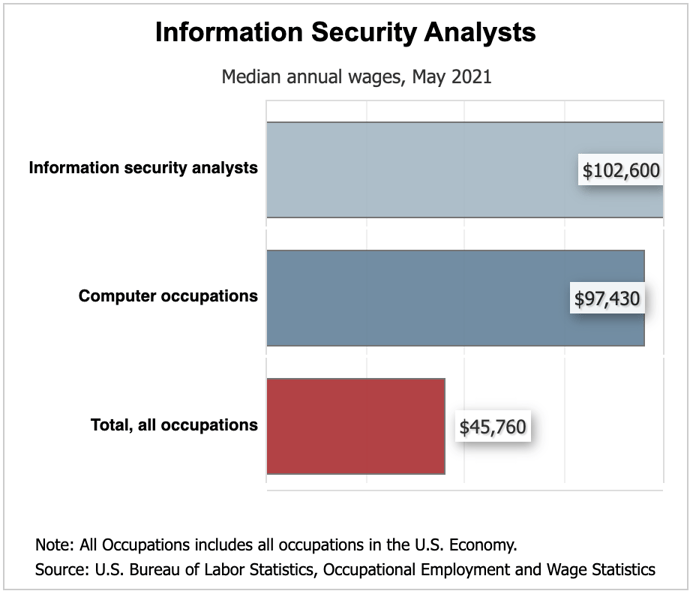
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, cybersecurity jobs pay an average salary of $102,600 per year which is significantly higher than the national average of $45,760. The top 10% of cybersecurity professionals earn over $165,920 per year, which is more than three times the national average.
Like all jobs, cybersecurity salaries can vary depending on the job and industry. The highest-paying industries for cybersecurity professionals include information, finance and insurance, and management of companies and enterprises.
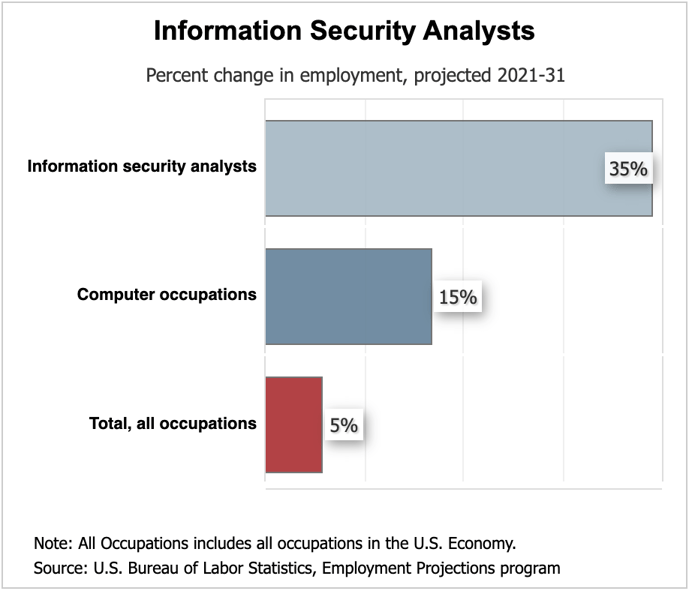
Demand for cybersecurity professionals is expected to grow rapidly in the coming years. The Bureau of Labor Statistics projects 35% growth from 2021 to 2031 which is much faster than the average for all other occupations.
Career outlook for cybersecurity professionals is excellent and salaries are likely to continue to increase.
What Degree is Best for Cybersecurity?
Pursuing a cybersecurity degree is oftentimes the first step in beginning a career in cybersecurity. Choosing the best degree program can be challenging given the number of options available.
The best cybersecurity degrees provide comprehensive understanding of the various aspects of cybersecurity like network security, cryptography, ethical hacking, security operations, cybercrime, forensics, policy, and compliance. Whenever possible, hands-on training should be provided, enabling students to apply knowledge in real-world scenarios.
One of the most popular cybersecurity degrees is a Bachelor’s in Cybersecurity as it provides students with the necessary foundation in cybersecurity concepts while preparing them for cybersecurity positions through practical training in ethical hacking and cyber incident response.
For those who already have their Bachelor’s in Cybersecurity and wish to further their formal education, a Master’s in Cybersecurity is a great next step. A Master’s in Cybersecurity program will arm students with knowledge and practical experience – both must haves in a successful cybersecurity career.
Which Certifications are Best for a Cyber Security Career?
When the formal education route doesn’t make sense, cybersecurity certifications are excellent alternatives. They’ll equip participants with the necessary skills and knowledge to protect organizations from cyberattacks. Look for industry recognized certification programs like Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), and Certified Information Security Manager (CISM).
Which Bootcamps and Training Programs are Best for a Cyber Security Career?
Cybersecurity bootcamps and training programs are often complementary to certification programs and offer individuals intense and immersive learning experiences. Bootcamps are designed to quickly train individuals in all things cybersecurity (skills, knowledge, technology, etc.).
Bootcamps and training programs are particularly valuable for those looking to transition to cybersecurity or need to upskill in key areas.
Conclusion
Protecting your business from cyberthreats is a top priority for business leaders across the globe. Doing so successfully starts with understanding the basics of cybersecurity which we’ve outlined in this post. Your business’s success is relying on a soundproof cybersecurity strategy.
If you’re looking for help with cybersecurity for your business, contact Zog for an assessment today. Our experts can assess your current security posture and recommend solutions to help protect your business from cyber threats.


Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *